Determining universal markers of quality in abdominal surgery: an international evaluation
The complete results of GlobalSurg I will be available shortly when they are published in full. But in the mean time here’s a quick snapshot of our analyses!
is the most commonly performed operation worldwide
is the indication for surgery in a higher proportion of cases in middle and low human development index countries
is performed more frequently in lower income countries
About GlobalSurg 1
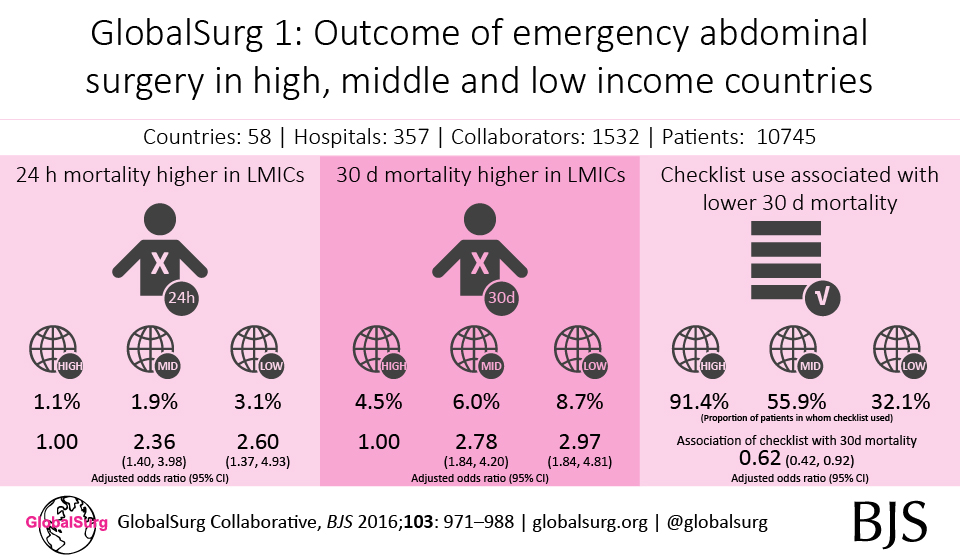
GlobalSurg I aimed to identify variation in outcome of emergency intra-abdominal surgery across international settings in order to determine whether globally relevant quality improvement strategies are needed within acute surgical units.
The study ran from July to November 2014. Contributors collected data on consecutive patients undergoing emergency intra-peritoneal surgery (excluding Caesarean section) over a two-week period in their local centres.
Patients were reviewed 24-hours post-surgery to determine whether they are dead or alive and any in-hospital complications by 30-days were determined. 30 datapoints per patient were collected and submitted to the study via a secure online website.
View the GlobalSurg 1 results in a snapshot
Project Protocol & Training
Data Collection
Data entry for GlobalSurg I was performed using the REDCap data collection system. Learn more about REDCap by clicking the image above.



